Creatine 101: Everything to Know About This Powerful Supplement
By Andrew Heffernan
If you've so much as dipped a toe into the vast world of sports supplements, you've heard of creatine, the unassuming, inexpensive powder that has been popular among fitness folks for many years.
There's a reason for its enduring popularity: It works. "Supplementing creatine can help support improvements in power, strength, and lean mass when combined with exercise," says Paul Falcone, MS, senior scientist at LADDER. That makes it a go-to for anyone seeking a stronger, more muscular physique or faster, more explosive movement on the field. Here's everything you need to know about the fine powder with a cool-sounding name.*
Increase strength and power with the performance-enhancing blend of ingredients (including creatine) in LADDER Pre-Workout.
.
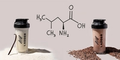
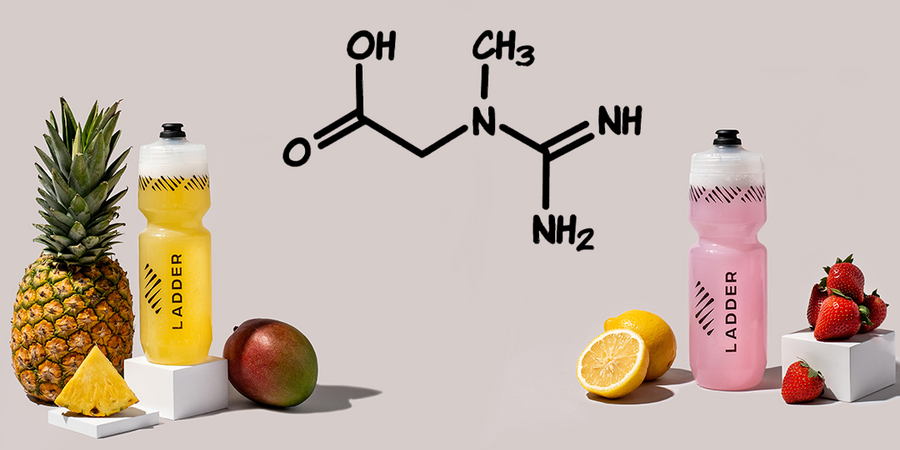
What is creatine?

Creatine is a compound usually found in red meat and seafood that is stored in the body as phosphocreatine, which provides your muscles with energy.
"This can mean everything from short bursts of intense exercise to a simple increase in movement, such as going from sitting to standing and walking," explains Falcone.
So if you're exercising, creatine can help on your heaviest lifts and your fastest sprints. Outside the gym, it's your primary energy source if you need to catch a toddler before he falls off the couch or regain your footing after you slip on some ice.
Nearly all your body's creatine is stored in your muscles — though there are trace amounts in your liver, brain, and kidneys.
.
Why do people use creatine?
Several factors influence the amount of creatine you store, including:
- Your diet: Meat is the primary dietary source of creatine, so vegetarians typically have less creatine than meat-eaters.
- Your muscle mass: People with more muscle mass store more creatine.
So creatine levels aren't fixed, and they vary from person to person. That's part of why supplementation can help: Storage capacities are limited, and your levels more than likely could use some topping off.
Supplementation keeps your creatine levels up — high enough to help increase power during your heaviest, most challenging workouts.
.
How does creatine improve exercise performance?

Creatine, a key ingredient in LADDER Pre-Workout, works to help promote muscle growth, strength, and performance in several ways:*
1. It provides fuel for your muscles
Specifically, creatine supports activities requiring strength and power.
Contrary to fitness myth, creatine is not a hormone or a drug. Rather, it's a fuel for movement — not unlike carbohydrates and fats — and it has been shown to be safe in studies going back decades.
2. It helps support muscle growth
Consuming creatine can help users train harder (do more reps), which can lead to greater muscle gains. Increasing total work volume is key to supporting muscle growth.*
3. It helps reduce the breakdown of muscle tissue following exercise
Like a classic car, muscle tissue is in a constant state of breakdown and repair. Growth occurs when muscular anabolism — the growing of new tissue — exceeds catabolism — breakdown. Creatine may help slow down catabolism, allowing anabolism to catch up and overtake it, leading to more muscle.*
4. It may help reduce levels of myostatin
Elevated levels of the protein myostatin can slow new muscle growth. Creatine has been studied for its effects on myostatin. Creatine appears to help reduce myostatin when combined with resistance training, potentially leading to more growth.
.
How does creatine work?
Creatine improves athletic performance in several ways by increasing the availability of creatine phosphate in muscles.
If you took high-school biology, you may remember that all human activity — from lifting weights to walking to breathing to reading this post — is ultimately powered by adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Well, your body has many ways of producing ATP, but the most accessible form of this vital fuel resides directly in your muscles as ATP-CP, otherwise known as creatine phosphate.
This storehouse of ATP is always at the ready when you need quick energy: If ever you need to run from a burning building, catch a falling vase, or power a long drive down the fairway, the ATP-CP in your muscles has your back. A hard set of squats, curls, chin-ups, or push-ups benefit from it, too.
The trouble is, even bulked-up bodybuilders can only store a relatively small amount — about 160 grams — of creatine in their muscles. That's why you can only sustain a truly maximal effort for a few seconds before you have to slow down: your muscles are literally out of the fuel they need for high-octane activities.

Top those stores off, however, and you may be able to squeeze a few more reps out of every tough set you perform in the gym. You may be able to get off the line a little faster on the track, make a quick burst to return an inbound ball on the tennis court.*
And that's more or less how creatine works. A 2012 paper, published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Medicine concluded that "creatine supplementation has the most pronounced effect on short duration (less than 30 seconds) high intensity intermittent exercises." Lifting weights may be the quintessential example of that type of exercise — though short sprints, activities requiring throwing (baseball, or field events like putting the shot), and sports with lots of starting and stopping (like American football) — also fit the bill.
While there isn't much supporting research, there may also be some advantages to taking creatine when performing aerobic exercises like long-distance running, cycling, or swimming. Creatine seems most likely to help during the higher-intensity portions of aerobic activities: a steep climb on the bike, the final kick of a 5K.*
.
How does creatine help muscle gain?
Creatine helps you do more of the activities that help your muscles grow: More reps and sets and more weight lifted in the gym. Over time, that additional work translates into more muscle.
.
Other health benefits of creatine
Creatine may have additional benefits, many of them neurological:*
1. Creatine may help fight age-related muscle loss
Muscle loss — sarcopenia — begins around age 40, and, in sedentary people, can continue unabated at a rate of nearly 1% per year after age 50, taking with it a good deal of the strength, vitality, and function of youth. Creatine has been shown to help combat muscle loss — both in conjunction with a strength-building program and in a few studies, on its own.
2. Creatine might help reduce risk factors associated with falling
Older adults taking creatine have shown better results on leg-strength tests that are correlated with better balance, suggesting that creatine may help safeguard against falling.*
.
When should I take creatine?

Unlike caffeine, creatine isn't immediately effective: it can take up to three to four weeks depending on initial creatine stores of taking the supplement consistently to see results. So it's important to take the supplement consistently. It doesn't matter when you take it during the day — morning, evening, before or after your workout — but some people find it convenient to take it as part of a pre-workout supplement so they are sure to get it regularly.
If you're eager to experience the benefits of creatine as quickly as possible, you can experiment with a loading phase — in which you take about 20 grams of creatine daily for a week to 5 to 7 days before dialing back to a maintenance dose of 3 to 5 grams daily.
Loading creatine isn't necessary to experience its effects, but you may experience them sooner if you do.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.